Pythagorean Theorem
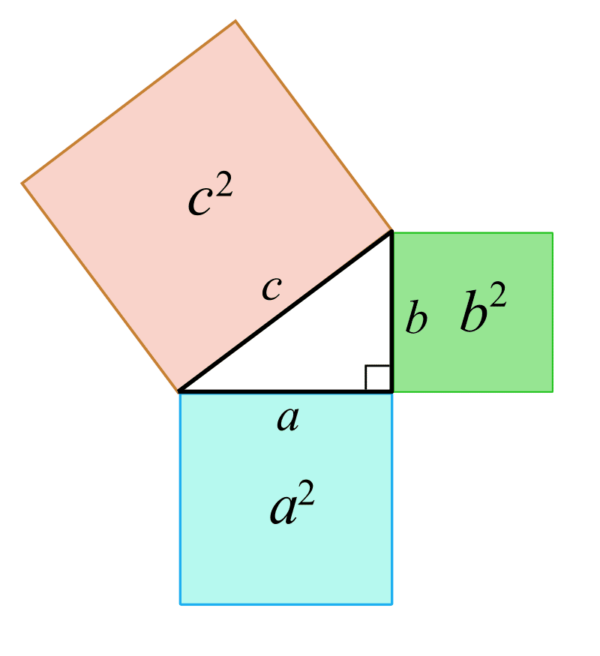
Image courtesy: wikimedia.org
In the previous blog, we learned about triangles and their properties as well as how to locate a triangle's area and a missing angle. This blog teaches us how to locate the triangle's missing side.
The Pythagorean Theorem, created by Pythagoras of Samos, can be used to solve for the missing sides of a right triangle. It states that the sum of the squares of the legs of the triangle is equal to the square of the hypotenuse.
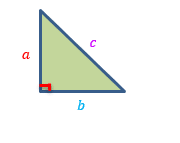
Figure #1
Figure #2
The theorem can be written as
![]()
Where ![]() and
and ![]() represent either of the legs, and
represent either of the legs, and ![]() , the hypotenuse.
, the hypotenuse.
Using this theorem, the solution for each side can also be solved as
![]()
![]()
![]()
Now that we have talked a bit about what the Pythagorean Theorem can be used for, let us examine at one of the many ways we can derive this formula.
Pythagorean Theorem Proof
(Go To Table Of Contents)
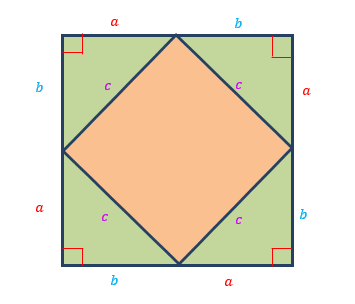
Figure #3
Look at Figure #3. We have a small green square inscribed in a larger beige square. The small green square has side lengths ![]() . Since the green square is inscribed in the beige square, it creates 4 identical right triangles with the legs measuring
. Since the green square is inscribed in the beige square, it creates 4 identical right triangles with the legs measuring ![]() and
and ![]() , and a hypotenuse measuring
, and a hypotenuse measuring ![]() . Using this information, we can start creating equations to solve for each side of the right triangles.
. Using this information, we can start creating equations to solve for each side of the right triangles.
Let’s first find the area of the beige square.
The area of a square is
![]()
The length of the square is equal to ![]() .
.
The width, since all sides of a square are equal, is also ![]() . So,
. So,
![]()
Distributing, we get
![]()
The area of the green square is
![]()
![]()
Next, let’s get the areas of the triangles. The area of a triangle is
![]()
Finding the area of one of the triangles, we can see that the base is ![]() and the height is
and the height is ![]() .So, the area can be represented as
.So, the area can be represented as
![]()
Since all 4 triangles are identical, we can obtain the total area of all four triangles by multiplying the area of 1 triangle by 4.
![]()
![]()
Using this new information, we can form another equation for the total area of the beige square. We can add the areas of the 4 right triangles to the area of the green square to get the total area of the beige square.
![]()
![]()
We now have two equations for the area of the beige square. We have
![]()
and
![]()
Now we can set both equations equal to each other and solve for ![]()
![]()
![]()
Subtracting ![]() from both sides we get
from both sides we get
![]()
Simplifying, we get
![]()
Now that we are done proving the Pythagorean Theorem, let’s apply it to some examples.
Book a Free Consultation Now!
To Learn more about Trigonometry tutoring at FPLA schedule a free consultation.
Examples
(Go To Table Of Contents)
Find the missing side, ![]() , of each given triangle
, of each given triangle
#1
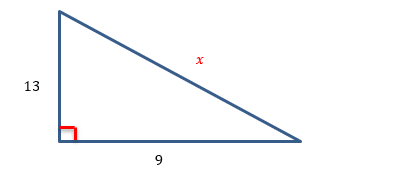
Figure #4
Remember:
The Pythagorean Theorem states,
![]()
Where ![]() and
and ![]() are the legs and
are the legs and ![]() is the hypotenuse.
is the hypotenuse.
Using the theorem, we can create the following equation for the triangle in Figure #4:
![]()
![]()
Simplifying, we get
![]()
![]()
Isolating ![]() we get
we get
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
#2
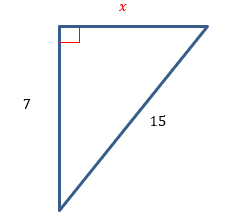
Figure #5
In Figure #5, we are missing the value of one of the legs of the triangle. To solve for ![]() , we can create the equation:
, we can create the equation:
![]()
Simplifying, we get
![]()
![]()
Isolating ![]() we get
we get
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Author: Mr. Vernon Sullivan, is a tutor at FPLA Miami, FL HQ premier 1-on-1 tutoring center. He teaches Algebra, Geometry, Pre-Cal, ACT, SAT, SSAT, HSPT, PERT, ASVAB and other test prep programs.
Mrs. Emimmal Sekar and Mr. Arikaran Kumar Proofread this article. Mr. Arikaran Kumar manages the website and the social media outreach.
